Toenail Fungus and Diabetes
Toenail Fungus
People with diabetes are twice as likely to develop toenail fungus. Diabetics may not notice symptoms of nail fungus because of reduced circulation. This makes it difficult for people with diabetes to detect damage to the nails. They should check their feet daily and take proper care of their toenails to prevent a serious infection. If left untreated, toenail ailment may become painful, thick, and sharp. It can even dig into the skin of the foot.
Diabetics are more likely to develop toenail fungus than people without the disease. This happens because people with diabetes frequently have nerve damage that makes them susceptible to injury. Furthermore, they may not be aware of an injury to a toenail. If this happens, they may not notice that it is infected, which allows fungus to get a foot infection. This infection may also lead to secondary infections of the foot.
Diabetic patients are also at a higher risk of toenail fungus. The condition is more likely to affect diabetics, who are already susceptible to foot ulcers. The infection can lead to amputation if it is not treated appropriately. As a result, it is important to see a podiatrist for treatment. Toenail fungus is also associated with diabetes mellitus, which is why it’s so important to care for your feet properly.
Crystal Flush Toenail Fungus Expert Review
While toenail fungus is generally harmless, it is best to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions about taking care of your feet. This includes keeping your feet clean and dry. Always soak your toenails before cutting them. If your toenails are thick or cracked, the fungus can spread to the foot and cause a secondary infection. If left untreated, the fungus will spread to other toenails.
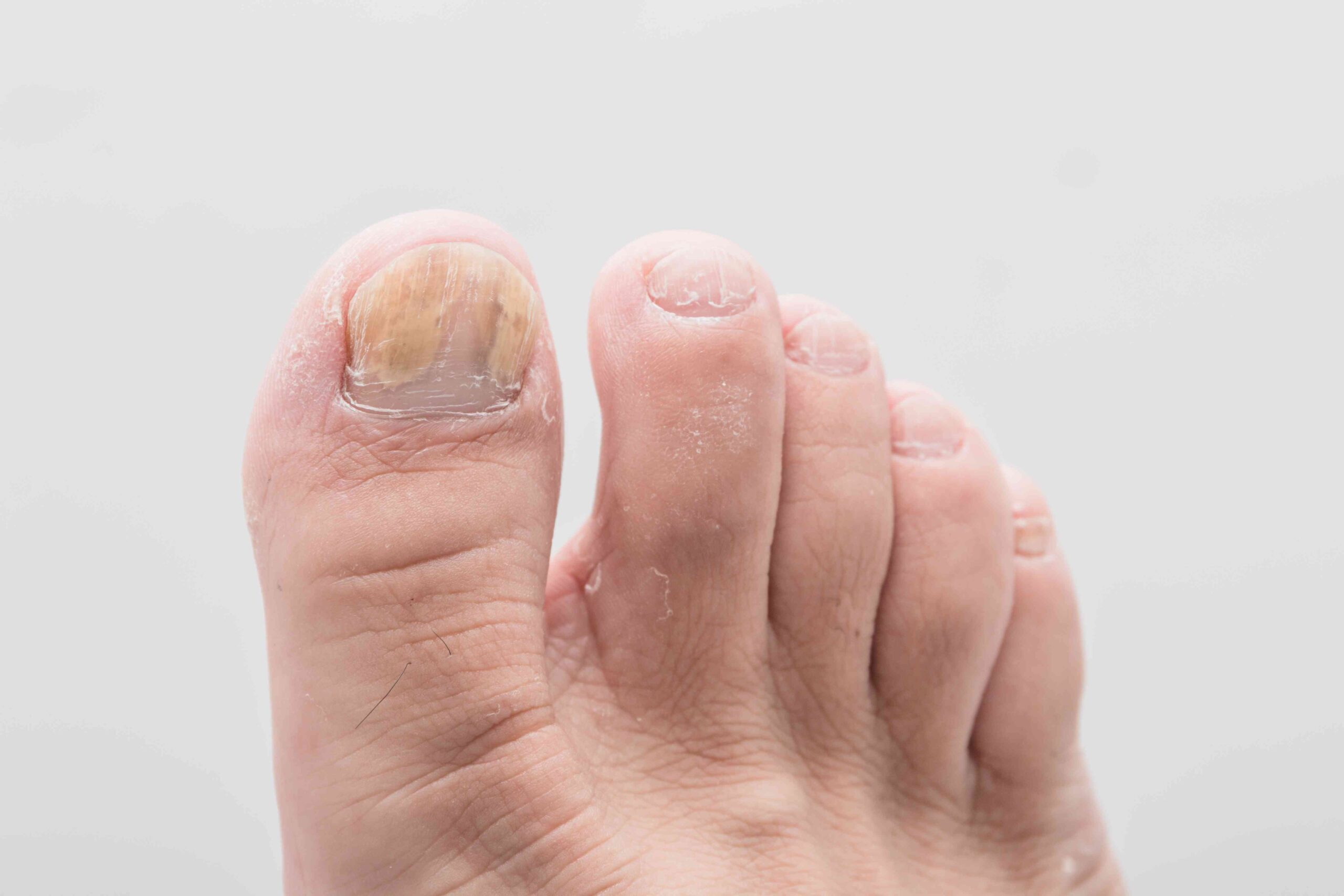
Toenail Fungus and Diabetes
People with diabetes should visit a podiatrist regularly to monitor for symptoms of toenail fungus. This way, the doctor can watch out for any symptoms and prescribe the right treatment for the patient. In severe cases, they may have to administer a more aggressive treatment. So, the best course of action for diabetic patients is to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Diabetes patients should make sure they take good care of their feet. A foot that is free of toenail fungus can be infected with a toenail fungus. During a period of diabetic-induced nerve damage, a person with diabetes is at increased risk of toenail fungus. They may also have a higher risk of developing a secondary infection if their toenails are injured.
Infections of the toenail can occur at any age. However, they are more common among older adults. As a result, aging nails become brittle and dry and cracks can allow fungi to enter the nail. In addition, a weakened immune system is another risk factor. In most cases, toenail fungus is not infectious, but it can spread from nail to nail.